^ 关注我,带你一起学GIS ^
注:当前使用的是 ol [9.2.4] 版本,天地图使用的key请到天地图官网申请,并替换为自己的key
 前言
前言
❝在GIS开发中,使用OpenLayers 模拟海平面上升的视觉效果。通过动态调整海平面高度,用户可以直观地看到哪些地区可能受到海平面上升的威胁,从而更好地理解和评估环境风险。使用 MapTiler Terrain-RGB tiles 瓦片和ol/source/Raster数据源,开发者可以模拟不同海拔高度下的海平面变化,直观地展示海平面上升对地理环境的潜在影响。
本文来源于OpenLayers官方例子,详情可参考官网:https://openlayers.org/en/v9.2.4/examples/sea-level.html
1. 前期准备
例子使用maptiler地图切片服务和地形服务数据进行展示,在进行地图开发前,如果还没有地图开发的key值,需要到maptiler官网申请key。
官网地址:https://cloud.maptiler.com如果之前未注册过账号,可以选择使用邮箱登录或谷歌账号登录,进入官网后,填写一些基本信息,进入到产品界面,如下图点击**[API Keys]**就可以看到自己的key值。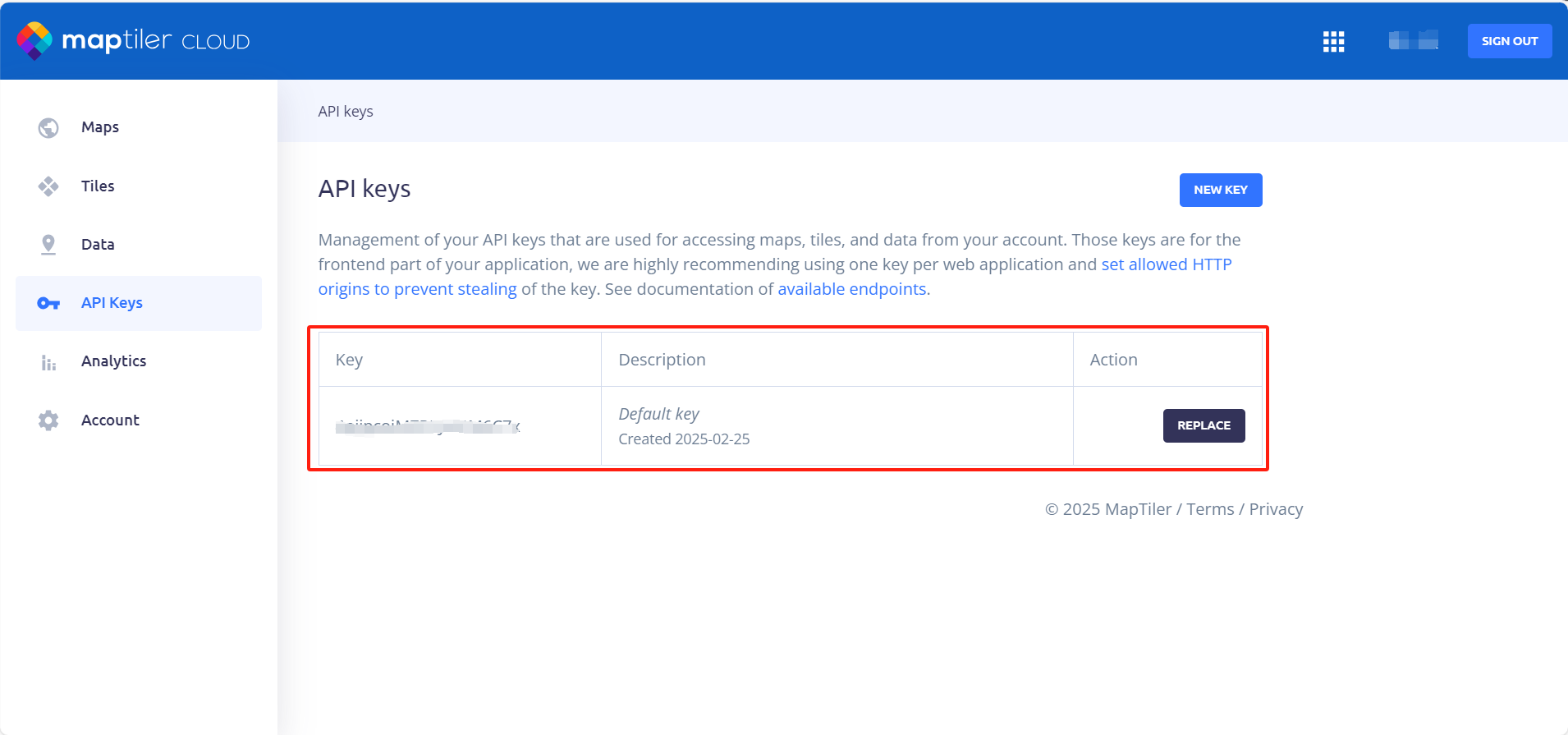
2. 地图坐标
在使用洪水淹没分析时,应将地图坐标系改为投影坐标系,如例子中使用的是墨卡托投影坐标系。如果使用地理坐标系则无法正常显示洪水淹没效果。
view: new ol.View({
center: ol.proj.fromLonLat([120.831, 31.160]),
zoom: 8,
worldsWrap: false,
minZoom: 1,
maxZoom: 20,
projection: 'EPSG:3857',
})
3. 洪水淹没函数
flood 函数的作用是根据像素的高程数据(海拔高度)和海平面高度(data.level),判断某个区域是否会被海水淹没,并将淹没区域用特定的颜色(浅蓝色)标记出来。未被淹没的区域则会被设置为透明。这个函数通常用于 地图可视化,特别是在模拟海平面上升、洪水淹没等场景中。它可以处理像素数据,动态生成淹没效果。
// 模拟洪水淹没
function flood(pixels, data) {
const pixel = pixels[0]
if (pixel[3]) {
const height = -10000 + (pixel[0] * 256 * 256 + pixel[1] * 256 + pixel[2]) * 0.1;
if (height <= data.level) {
pixel[0] = 134
pixel[1] = 203
pixel[2] = 249
pixel[3] = 255
} else {
pixel[3] = 0
}
}
return pixel
}
4. 添加底图和高程服务
使用ol.source.XYZ切片数据源创建maptiler高程数据源,然后将其添加到ol.source.Raster栅格数据源中。创建完成底图服务和影像图层后将其添加到地图对象中。
// 高程数据
const elevation = new ol.source.XYZ({
url: 'https://api.maptiler.com/tiles/terrain-rgb-v2/{z}/{x}/{y}.webp?key=' + maptilerKey,
tileSize: 512,
maxZoom: 14,
crossOrigin: "",
interpolate: false
})
// 栅格图层
const raster = new ol.source.Raster({
sources: [elevation],
operation: flood
})
// maptiler地图服务
const maptilerLayer = new ol.layer.Tile({
source: new ol.source.XYZ({
url: 'https://api.maptiler.com/maps/streets-v2/{z}/{x}/{y}.png?key=' + maptilerKey,
tileSize: 512,
maxZoom: 22,
})
})
// 高程服务
const imageLayer = new ol.layer.Image({
source: raster,
opacity: 0.6
})
map.addLayer(maptilerLayer)
map.addLayer(imageLayer)
5. 洪水淹没分析
使用滑动条更改高程值,在地图上进行洪水淹没动态分析,并显示高程值,可以看到淹没范围随着高程值得改变而动态变化。
// 监听高程值变化
const seaChange = document.querySelector(".sea-input")
// 更新显示高程值
const seaOutput = document.querySelector(".sea-output")
seaChange.addEventListener("input", (evt => {
seaOutput.innerText = seaChange.value
raster.changed()
}))
seaOutput.innerText = seaChange.value
raster.on("beforeoperations", event => {
event.data.level = seaChange.value
})
6. 完整代码
其中libs文件夹下的包需要更换为自己下载的本地包或者引用在线资源。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>OpenLayers 模拟海平面上升的视觉效果</title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../../libs/css/ol9.2.4.css">
<script src="../../js/config.js"></script>
<script src="../../libs/js/ol9.2.4.js"></script>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
font-size: 14px;
font-family: '微软雅黑';
}
html,
body {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
#map {
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
bottom: 0;
width: 100%;
}
#top-content {
position: absolute;
width: 100%;
height: 50px;
line-height: 50px;
background: linear-gradient(135deg, #ff00cc, #ffcc00, #00ffcc, #ff0066);
color: #fff;
text-align: center;
font-size: 32px;
}
#top-content span {
font-size: 32px;
}
.state {
position: absolute;
bottom: 10px;
line-height: 30px;
background: linear-gradient(135deg, #ff00cc, #ffcc00, #00ffcc, #ff0066);
color: #fff;
display: flex;
height: 30px;
width: 25%;
left: 50%;
transform: translateX(-50%);
border-radius: 5px;
}
.state-item {
width: 50%;
text-align: center;
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: bold;
}
.sea-input {
vertical-align: text-bottom;
}
.sea-output {
display: inline-block;
width: 30px;
}
.location-item {
text-align: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="top-content">
<span>OpenLayers 模拟海平面上升的视觉效果</span>
</div>
<div id="map" title=""></div>
<div class="state">
<div class="state-item">
<label for="">海拔:</label>
<input class="sea-input" type="range" value="1" min="0" max="100" step="1"></input>
</div>
<div class="state-item location-item">
+<label for="" class="sea-output"></label>m
<label class="location">当前定位:上海</label>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<script>
const map = new ol.Map({
target: "map",
loadTilesWhileInteracting: true,
view: new ol.View({
center: ol.proj.fromLonLat([120.831, 31.160]),
zoom: 8,
worldsWrap: false,
minZoom: 1,
maxZoom: 20,
projection: 'EPSG:3857',
}),
layers: [],
// 地图默认控件
controls: ol.control.defaults.defaults({
zoom: false,
attribution: true,
rotate: true
})
})
// 模拟洪水淹没
function flood(pixels, data) {
const pixel = pixels[0]
if (pixel[3]) {
const height = -10000 + (pixel[0] * 256 * 256 + pixel[1] * 256 + pixel[2]) * 0.1;
if (height <= data.level) {
pixel[0] = 134
pixel[1] = 203
pixel[2] = 249
pixel[3] = 255
} else {
pixel[3] = 0
}
}
return pixel
}
// 高程数据
const elevation = new ol.source.XYZ({
url: 'https://api.maptiler.com/tiles/terrain-rgb-v2/{z}/{x}/{y}.webp?key=' + maptilerKey,
tileSize: 512,
maxZoom: 14,
crossOrigin: "",
interpolate: false
})
// 栅格图层
const raster = new ol.source.Raster({
sources: [elevation],
operation: flood
})
// maptiler地图服务
const maptilerLayer = new ol.layer.Tile({
source: new ol.source.XYZ({
url: 'https://api.maptiler.com/maps/streets-v2/{z}/{x}/{y}.png?key=' + maptilerKey,
tileSize: 512,
maxZoom: 22,
})
})
const imageLayer = new ol.layer.Image({
source: raster,
opacity: 0.6
})
map.addLayer(maptilerLayer)
map.addLayer(imageLayer)
// 监听高程值变化
const seaChange = document.querySelector(".sea-input")
// 更新显示高程值
const seaOutput = document.querySelector(".sea-output")
seaChange.addEventListener("input", (evt => {
seaOutput.innerText = seaChange.value
raster.changed()
}))
seaOutput.innerText = seaChange.value
raster.on("beforeoperations", event => {
event.data.level = seaChange.value
})
</script>
❝
OpenLayers示例数据下载,请在公众号后台回复:ol数据
全国信息化工程师-GIS 应用水平考试资料,请在公众号后台回复:GIS考试
❝
GIS之路公众号已经接入了智能助手,欢迎大家前来提问。
欢迎访问我的博客网站-长谈GIS:
http://shanhaitalk.com
都看到这了,不要忘记点赞、收藏+关注 哦!
本号不定时更新有关 GIS开发 相关内容,欢迎关注 


