^ 关注我,带你一起学GIS ^
 前言
前言
❝在GIS开发中,经常需要进行数据的转换处理。在之前的文章中讲了如何使用GeoTools读取Shapefile数据,并且展示了【五种】将Shapefile数据导入PostGIS空间数据库的方式,但是还缺少Shapefile数据转换来源的操作。
本篇教程在之前文章的基础上讲解如何将GeoJSON数据转换为我们熟悉的Shapefile文件格式。
开发环境
本文使用如下开发环境,以供参考。
时间:2025年
GeoTools:34-SNAPSHOT
IDE:IDEA2025.1.2
JDK:17
1. 准备 GeoJSON 文件
GeoJSON是一种用于编码各种地理数据结构的格式,采用JSON方式表示。在WebGIS开发中,被广泛应用于数据传输和共享交换。
有关GeoJSON数据的详细介绍,请参考往期文章:GeoJSON 数据简介
由于GeoJSON测试数据内容过大,此处就不展示了。
2. 安装依赖
pom.xml文件在之前开发的基础上增加gt-geojson和jts-core两个依赖包。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-geojson</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JTS 几何库 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.locationtech.jts</groupId>
<artifactId>jts-core</artifactId>
<version>1.18.2</version>
</dependency>
3. 创建 Shp 要素结构
使用showOpenFile方法打开文件选择框,然后使用SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder动态构造要素结构。
// 设置外观
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(UIManager.getCrossPlatformLookAndFeelClassName());
// 选择json文件
File file = JFileDataStoreChooser.showOpenFile(".json",null);
if(file == null ){
System.out.println("GeoJSON 文件不正确,请检查?");
return;
}
// 存储要素
List<SimpleFeature> features = new ArrayList<>();
// 读取 GeoJSON
FeatureJSON featureJSON = new FeatureJSON();
SimpleFeatureCollection featureCollection;
try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file)){
featureCollection = (SimpleFeatureCollection) featureJSON.readFeatureCollection(fis);
}
// 获取要素schema,也就是要素数据结构
SimpleFeatureType featureType = featureCollection.getSchema();
// 要素特征构建器
SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder simpleFeatureTypeBuilder = new SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder();
simpleFeatureTypeBuilder.setName("County"); // 定义名称
simpleFeatureTypeBuilder.setCRS(DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84); // 定义坐标系
// 添加几何属性
simpleFeatureTypeBuilder.add("the_geom",featureType.getGeometryDescriptor().getType().getBinding());
// 添加所有属性字段
featureType.getAttributeDescriptors().forEach(descriptor -> {
if(!descriptor.getType().getBinding().isAssignableFrom(Geometry.class)){
simpleFeatureTypeBuilder.add(descriptor);
}
});
SimpleFeatureType SHAPE_TYPE = simpleFeatureTypeBuilder.buildFeatureType();
// 创建FeatureBuilder
SimpleFeatureBuilder featureBuilder = new SimpleFeatureBuilder(SHAPE_TYPE);
例子中可根据源数据结构动态创建字段,几何字段使用simpleFeatureTypeBuilder.add("the_geom",featureType.getGeometryDescriptor().getType().getBinding())此代码动态添加,如果确定几何字段类型,也可以直接使用simpleFeatureTypeBuilder.add("the_geom", MultiPolygon.class)方式添加。
对于非几何字段则通过方法getAttributeDescriptors获取所有源字段类型进行创建,在添加属性字段时将几何字段排除。
4. 创建 Shapefile
使用ShapefileDataStoreFactory工厂方法生产Shp,在createDataStore参数中将属性"create spatial index"设置为true表示为Shp数据创建空间索引。
// 选择shp路径
File shpFile = getNewShapeFile(file);
// 创建Shapefile
ShapefileDataStoreFactory factory = new ShapefileDataStoreFactory();
Map<String, Serializable> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("url", shpFile.toURI().toURL());
params.put("charset", "GBK");
params.put("create spatial index",Boolean.TRUE);
ShapefileDataStore dataStore = (ShapefileDataStore) factory.createNewDataStore(params);
dataStore.createSchema(featureCollection.getSchema()); // 应用定义好的Schema
dataStore.forceSchemaCRS(CRS.decode("EPSG:4326")); // 明确CRS
对于中文字段,需要设置字符集,以防出现乱码,此处将"charset"设置为"GBK",对于中文最好将字符集设置为"GBK",设置为"UTF-8"还是有可能难以正确解析。
在创建Shp对象时,还是需要指定坐标信息,否则转换结果将缺少坐标系统。在GIS软件中打开数据可以查看元素据信息,下图是未指定坐标系时在ArcMap中的打开情况。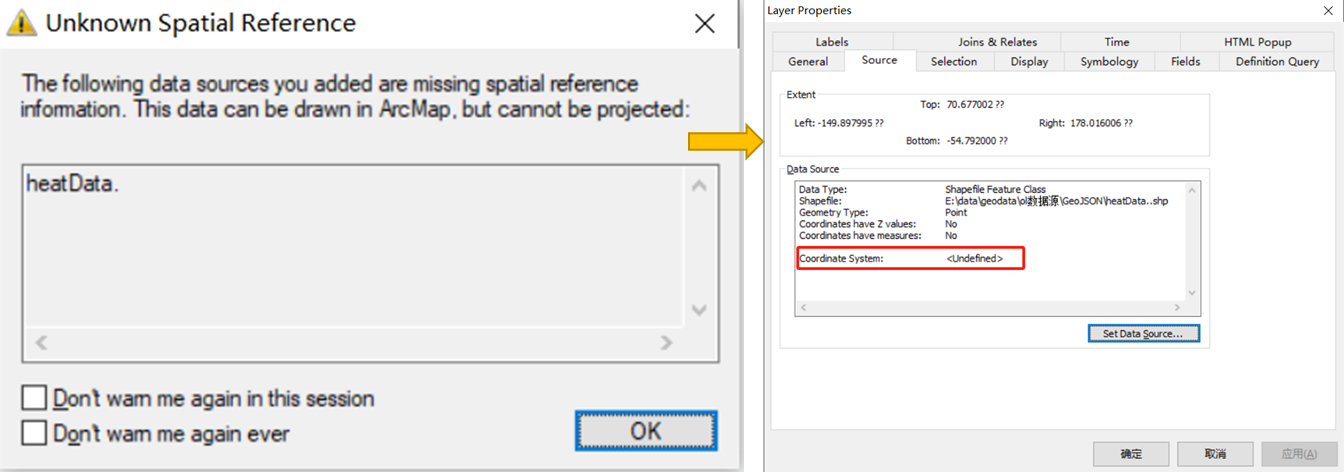
指定坐标系为4326后转换结果元数据信息,使用GIS软件ArcMap打开如下,可以看到此时显示正确。
5. 读取 GeoJSON 并写入 Shp
首先通过Transaction创建事务对象,准备提交数据。之后遍历要素集,根据源数据类型分别动态设置几何结构和属性结构。使用featureBuilder.set(SHAPE_TYPE.getGeometryDescriptor().getLocalName(), feature.getDefaultGeometry())代码添加几何字段。使用getAttributeDescriptors方法获取到属性字段集之后遍历其属性结构。
// 创建事务对象,准备提交数
Transaction transaction = new DefaultTransaction("create");
// 获取存储特征对象
String typeName = dataStore.getTypeNames()[0];
SimpleFeatureSource featureSource = dataStore.getFeatureSource(typeName);
// 准备写入数据到Shp文件
if(featureSource instanceof SimpleFeatureStore){
SimpleFeatureStore featureStore = (SimpleFeatureStore) featureSource;
// 准备要写入的特征集合
ListFeatureCollection collection = new ListFeatureCollection(SHAPE_TYPE);
// 复制要素特征
try(FeatureIterator<SimpleFeature> it = featureCollection.features()){
while (it.hasNext()) {
SimpleFeature feature = it.next();
// 重置 builder 准备构建新特征
featureBuilder.reset();
// 复制几何属性
featureBuilder.set(SHAPE_TYPE.getGeometryDescriptor().getLocalName(), feature.getDefaultGeometry());
// 复制其他属性
SHAPE_TYPE.getAttributeDescriptors().forEach(descriptor -> {
// 属性名称
String name = descriptor.getLocalName();
if(!descriptor.getType().getBinding().isAssignableFrom(Geometry.class)
&& feature.getAttribute(name) != null){
featureBuilder.set(name,feature.getAttribute(name));
}
});
SimpleFeature targetFeature = featureBuilder.buildFeature(null);
collection.add(targetFeature);
}
}
// 写入特征到 Shapefile
featureStore.setTransaction(transaction);
try{
// 写入特征到Shapefile
featureStore.addFeatures(collection);
transaction.commit();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
transaction.rollback();
}finally {
transaction.close();
}
System.exit(0);
}
// 显式释放资源
dataStore.dispose();
转换完成后使用GIS软件ArcGIS Pro打开属性表结构如下。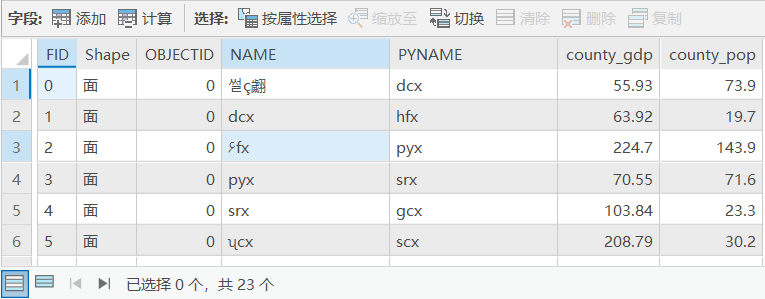
6. Shapefile 输出位置
使用getNewShapeFile方法选择Shp输出位置,最后输出的结果就是GIS开发中常用的Shp格式了。
// 提示输出Shapefilew文件位置
private static File getNewShapeFile(File jsonFile){
String path = jsonFile.getAbsolutePath();
String newPath = path.substring(0,path.length()-5)+".shp";
JFileDataStoreChooser chooser = new JFileDataStoreChooser(".shp");
chooser.setDialogTitle("保存ShapeFile");
chooser.setSelectedFile(new File(newPath));
int returnVal = chooser.showSaveDialog(null);
if(returnVal != JFileDataStoreChooser.APPROVE_OPTION){
System.exit(0);
}
File newFile = chooser.getSelectedFile();
if(newFile.equals(jsonFile)){
System.out.println("Error:不能替换" + jsonFile);
System.exit(0);
}
return newFile;
}
注:用于转换为Shp文件的GeoJSON数据,其中的几何类型必须要保持一致,而且只能有一种几何类型。
❝
OpenLayers示例数据下载,请在公众号后台回复:ol数据
全国信息化工程师-GIS 应用水平考试资料,请在公众号后台回复:GIS考试
❝
GIS之路公众号已经接入了智能助手,欢迎大家前来提问。
欢迎访问我的博客网站-长谈GIS:
http://shanhaitalk.com
都看到这了,不要忘记点赞、收藏+关注 哦!
本号不定时更新有关 GIS开发 相关内容,欢迎关注 


